Air gaging can be described as the use of air flow and air pressure to determine the size of measured part’s dimensions. Air gaging relies on the laws of physics, which states that the volume of flow and the pressure are inversely proportional. As the clearance between the flow and the part increases, the pressure decreases and as the clearance decreases the pressure around the part increases.
The working principle of all air gaging applications require requlated air flow through a restriction(orifice) prior to being expelled through the nozzles of the air tool. Maximum air flow occurs when the nozzle of air is unobstructed by the workpiece. The air pressure which is also called the back pressure is at a minimum. During the time when the part is being measured, Air flow through the nozzle diminishes and the pressure builds up around the measured part. When the nozzle is completely sealed by the measured part, the back pressure reaches to the same level with the requlated air supply. The values of pressure and the flow can be drawn as a graph to explain things further in detail.
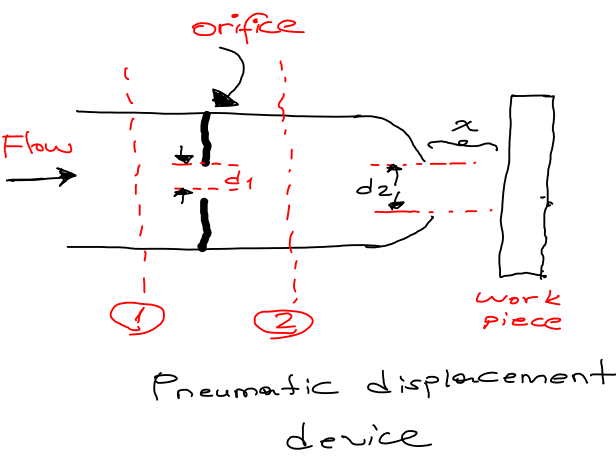
Consider the system shown above. Air is supplied at a constant pressure from the first region. The flow through the orifice and through the outlet of diameter d2 is governed by the seperation distance x between the outlet and the workpiece. The change in flow with x will be indicated by a change in the pressure downstream from the orifice p2. Thus, a measurement of this pressure may be taken as an indication of the seperation distance x. We assume the flow to be incompressible for the purposes of our analysis. The volumetric flow through the orifice may be represented by

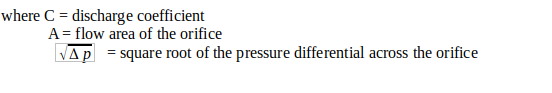
There are two orifices in our case, the one in the first section and the one between the nozzle and the workpiece. We will designate the first area A1 of the orifice and A2 of the orifice. Than the previous equation becomes.
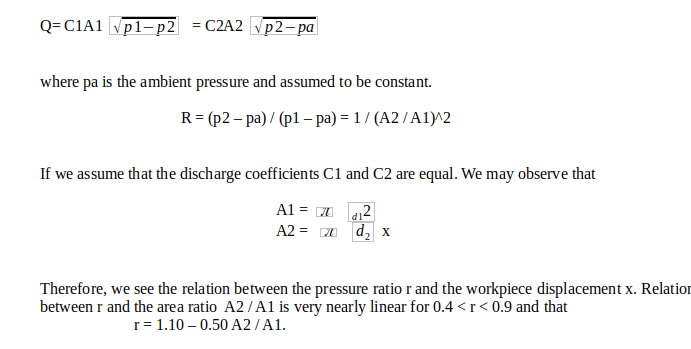
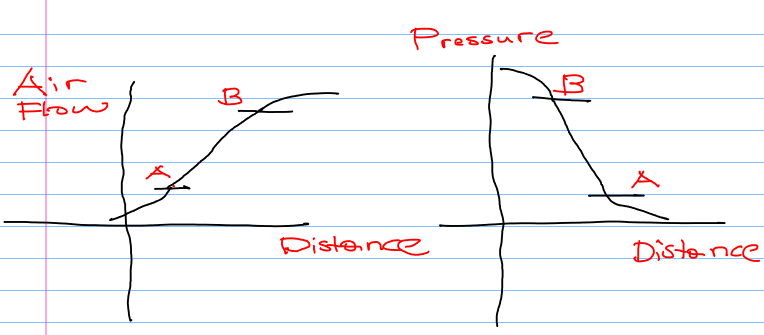
As the distance between the nozzle and the workpiece increase air flow increases and the pressure decreases around the workpiece. When this distance decreases the air flow decreases and the pressure increases. The linearity is well preserved around 0.4 < r < 0.9.
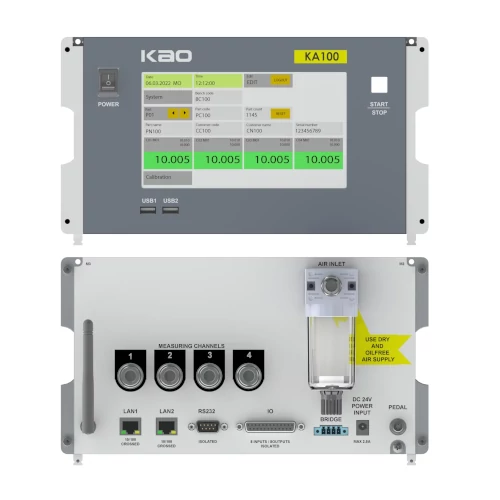
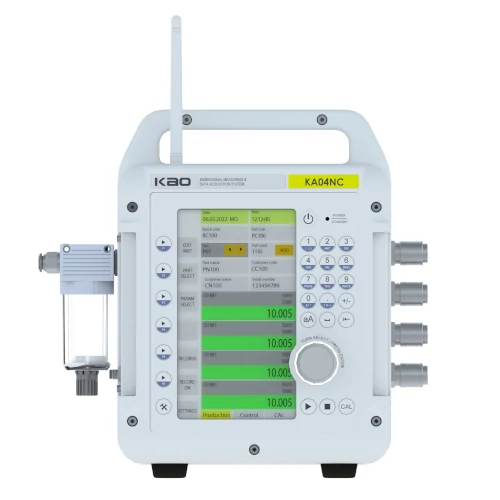
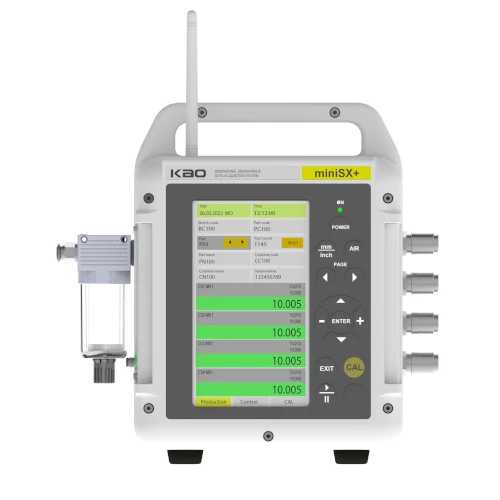
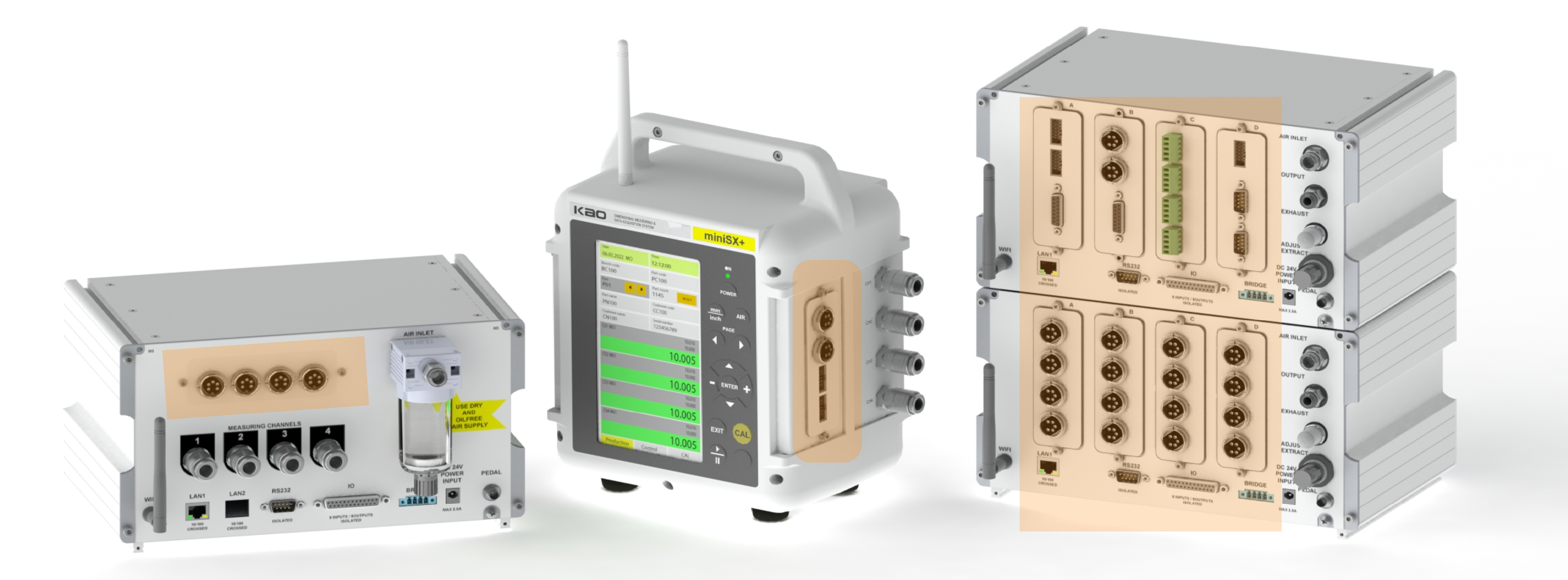
As Kao Metrology, our Air gaging instruments use the latest innovations in microchip technology to make fast and precise measurements. We use the latest chips and the sensors to measure your workpiece and deliver your results with industry standard formats. We produce Air gaging devices with as much channel as possible specific to your needs.